
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are PSCs produced by reprogramming somatic cells through overexpression of certain pluripotency markers ( Ye et al., 2013 Moradi et al., 2019). Although only embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are genuinely pluripotent, differentiated cells can also be converted to a pluripotent state ( Zakrzewski et al., 2019).
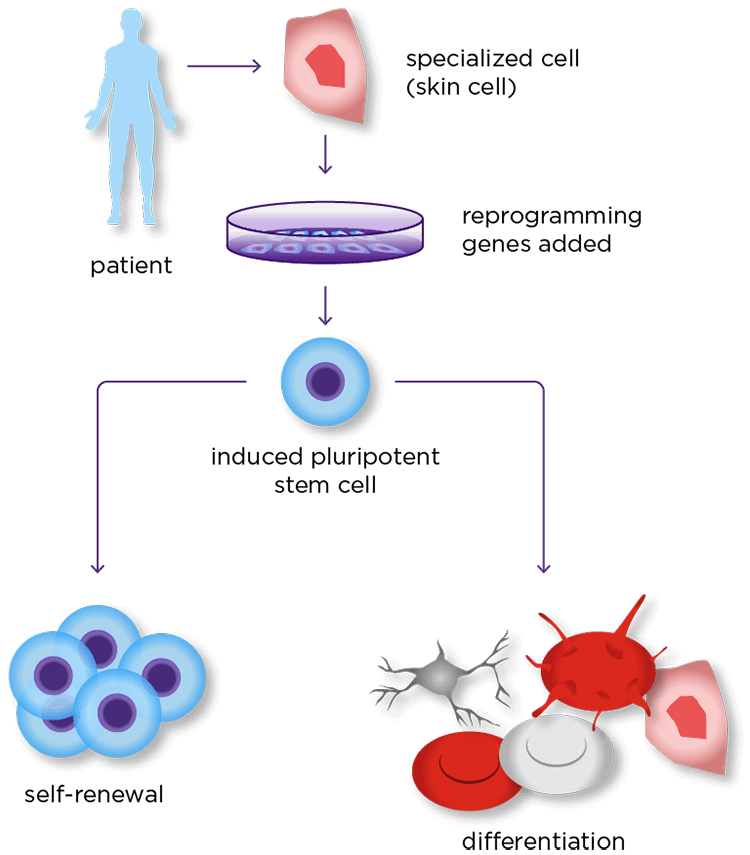
PSCs have two characteristics of self-renewal and pluripotency ( Romito and Cobellis, 2016). Accessibility of pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) with their vast potential for proliferation and differentiation provides new chances for basic research, disease modeling, drug discovery, and advancement of cell therapies ( Martin, 2017). Cell-based therapy is considered one of the most promising methods in modern medicine ( Aly, 2020). In recent years, major advances have been made in the field of stem cells and regenerative medicine ( Liu et al., 2020). We also present recent applications of iPSCs in the study and treatment of COVID-19. In this study, we discuss the different methods of generation of iPSCs as well as their respective advantages and disadvantages. iPSCs have become one of the most attractive and promising tools in this field by providing the ability to study COVID-19 and the effectiveness of drugs on this disease outside the human body. Therefore, researchers have been rigorously studying and examining all aspects of COVID-19 and potential treatment modalities and various drugs in order to enable the treatment, control, and prevention of COVID-19. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a disease that has endangered numerous human lives worldwide and currently has no definitive cure. Since iPSCs can be generated from somatic cells, they can be considered as valuable cellular resources available for important research needs and various therapeutic purposes. Studying these methods would be very helpful in developing an easy, safe, and efficient method for the generation of iPSCs. Different methods have been used to produce iPSCs, each of which has advantages and disadvantages. The availability and safety of iPSCs for therapeutic purposes require safe and highly efficient methods for production of these cells. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) exhibit an unlimited ability to self-renew and produce various differentiated cell types, thereby creating high hopes for both scientists and patients as a great tool for basic research as well as for regenerative medicine purposes. 5Iranian Tissue Bank and Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.4Department of Tissue Engineering and Applied Cell Science, School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.3Hematology and Cell Therapy Department, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.2Department of Stem Cells and Developmental Biology, Cell Science Research Center, Royan Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Technology, ACECR, Tehran, Iran.1Department of Biology, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.6 Technical University of Munich, School of Medicine & Health, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Institute Insure, German Heart Center Munich, Lazarettstrasse 36, 80636 Munich, Germany.Zahra Karami 1, Sharif Moradi 2, Akram Eidi 1, Masoud Soleimani 3,4 and Arefeh Jafarian 5*.6 Technical University of Munich, School of Medicine & Health, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Institute Insure, German Heart Center Munich, Lazarettstrasse 36, 80636 Munich, Germany.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
